
The purpose of co-employment is to allow businesses, especially small companies, to focus on core activities while ensuring HR compliance. It brings several benefits but also some risks that need to be managed through best practices. This article provides an in-depth look at what co-employment is, its advantages, as well as tips for managing risks and ensuring success.
Co-employment is an arrangement where two or more organizations share the legal responsibilities of employing staff. Typically, a company partners with a professional employer organization (PEO) or staffing agency and enters into a co-employment relationship.
In this setup, the client company maintains control over daily operations, roles, workplace culture while the PEO/agency handles HR administration like payroll, benefits, compliance.
In a co-employment agreement, the responsibilities are split between the client company and the co-employment partner, usually a professional employer organization (PEO) or staffing agency.
The client company retains control and authority over the day-to-day work and management of employees. Specifically, the client company handles:
Essentially, the client company continues to maintain the primary employer relationship, including overseeing job duties, providing supervision, and making personnel decisions.
The co-employment partner, often a PEO or a staffing agency, handles a range of administrative and compliance-focused HR responsibilities, including:
The specific services offered can vary depending on the provider, but in general the PEO/agency takes over the more administrative aspects of HR and employment compliance. This allows the client company to offload these tasks and focus more on core business operations.
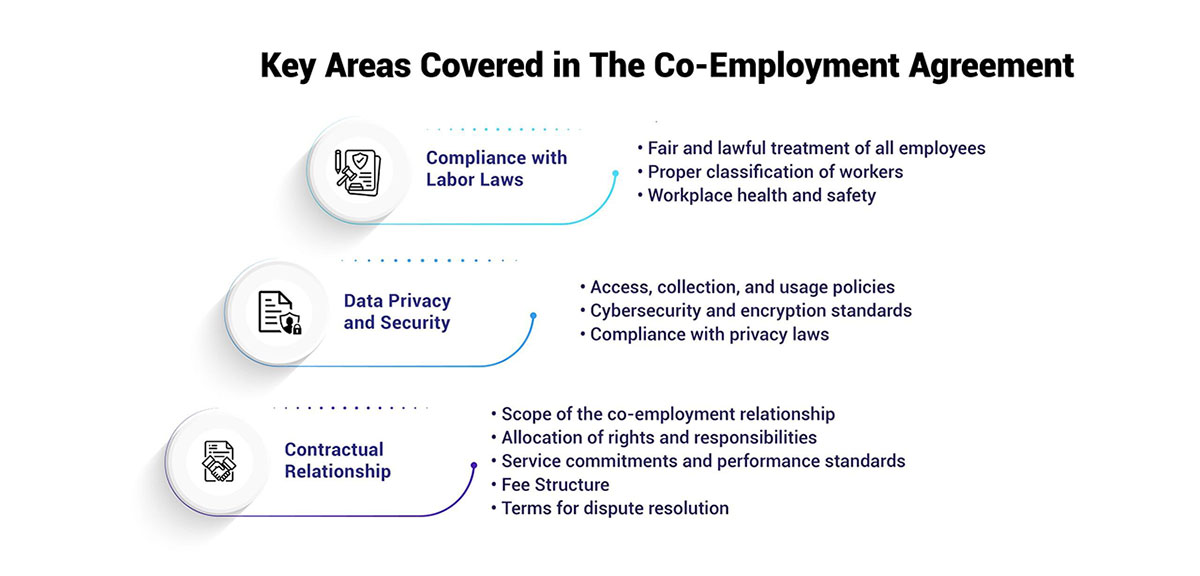
This section of the agreement outlines how both the client company and the co-employment partner will ensure compliance with all relevant employment laws and regulations at the federal, state, and local levels.
Areas addressed under labor law compliance typically include:
Having clear guidelines for employment law compliance is crucial for reducing legal risks and lawsuits. It also ensures workers are treated lawfully and have full access to their entitled rights and protections.
This section focuses on policies and procedures for protecting sensitive and confidential employee data handled by the co-employment partner. It typically covers:
Clear data handling guidelines preserve transparency while prioritizing employee privacy in the co-employment arrangement.
This section serves as the legal basis formalizing the functional, financial, and operational terms between the client company and the co-employment services provider. Key elements covered include:
Defining these contractual details reduces ambiguity about the functionality of the co-employment setup while ensuring consensus and clarity from a legal perspective.
The main differences between co-employment and outsourcing:
In co-employment, the client company oversees employees' day-to-day work. The PEO handles HR functions but doesn't manage operations.
In outsourcing, the vendor has control over operations and processes. The client has little input into how work gets done.
In co-employment, employers and PEO share duties. The client handles business operations, PEO handles HR administration.
In outsourcing, the vendor takes full responsibility for the outsourced function. The client simply receives the end product/service.
In co-employment, the client and PEO share employment-related liability.
In outsourcing, the liability lies primarily with the vendor since they are responsible for operational risks.
There are significant advantages to entering a co-employment arrangement:
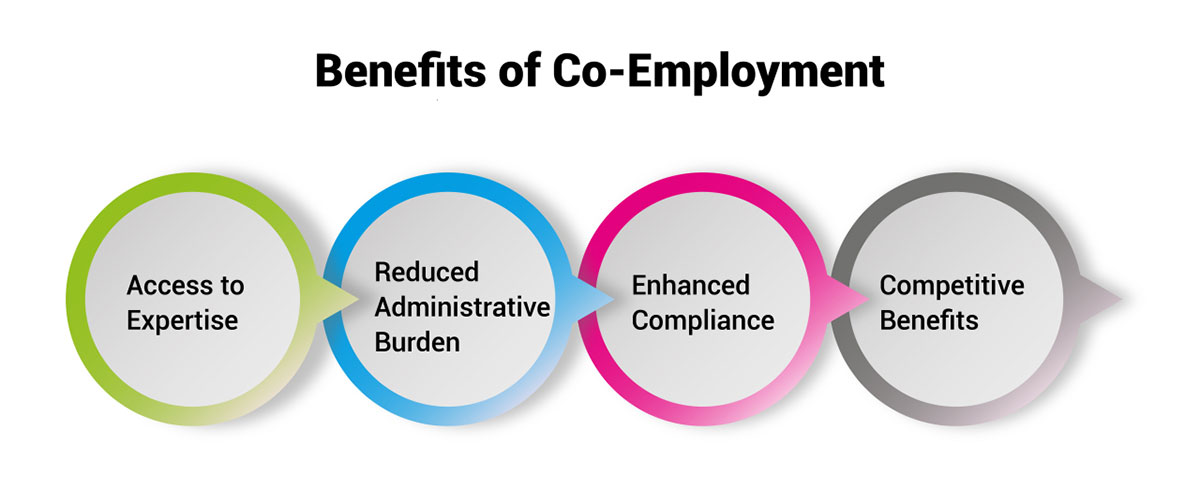
Co-employment arrangements provide businesses with valuable access to specialized HR and legal expertise that they likely lack in-house. By partnering with a professional employer organization (PEO) or staffing agency, companies gain support from professionals who exclusively focus on managing critical HR functions.
These co-employment partners have extensive knowledge related to key areas such as payroll processing, benefits administration, recruitment and hiring, employee training, performance management, and staying compliant with labor laws. Their expertise helps businesses avoid costly pitfalls and ensures that best practices are followed when it comes to nearly all aspects of workforce management.
For example, a PEO can leverage their dedicated legal team to ensure that a client company's policies and procedures align with the latest employment regulations across all jurisdictions where they operate. Or they may use their HR specialization to overhaul and optimize the client's benefits packages to be more competitive within their industry.
Access to this level of expertise is invaluable for businesses who lack specialized HR/legal staff internally. It allows them to effectively manage their workforce while benefiting from professional guidance around mission-critical people operations.
By entering a co-employment arrangement, companies can significantly reduce the administrative burden associated with managing HR responsibilities in-house. Tedious tasks like payroll processing, benefits enrollment, compliance paperwork, and tax filings can be offloaded to a PEO or staffing partner.
This frees up substantial time and resources for the client company, allowing leadership and internal HR staff to focus more on forward-thinking strategic initiatives, employee engagement, and fostering an optimal culture. Rather than getting bogged down with repetitive admin tasks, they can now spend more time on big-picture workforce planning and management.
Consider a growing startup that urgently needs to scale up hiring but lacks payroll infrastructure. Partnering with a PEO provides immediate administrative support, so the startup can achieve its growth goals without navigating the complexities of managing payroll, taxes, and compliance solo.
Or take a small business looking to offer more robust benefits without excess administrative work. By leveraging a co-employer, they can easily provide enhanced health insurance, retirement savings plans, and other perks to attract talent.
The reduction in the administrative burden is a major advantage of co-employment arrangements for resource-constrained companies.
Maintaining ongoing compliance with the ever-evolving patchwork of employment laws and regulations represents a monumental challenge for HR teams. But non-compliance can result in hefty lawsuits, fines, and damage to an employer's reputation.
Fortunately, co-employment partnerships allow businesses to meet compliance requirements more easily. PEOs and staffing agencies possess extensive legal and compliance expertise since remaining updated on the latest regulations is a fundamental aspect of their role.
These partners handle compliance with wage and hour rules, workplace safety standards, discrimination laws, employee leave policies, health insurance mandates, and much more. This significantly reduces any compliance-related risks for their clients across all jurisdictions where they operate.
For example, as laws regarding independent contractors and freelance workers continue to fluctuate state-by-state, co-employment arrangements help companies adapt accordingly without fear of misclassifying workers.
Many small businesses simply can’t match the types of robust health insurance plans, retirement savings options, and other employee perks offered by large enterprise corporations. This harms their ability to stand out and attract top-tier talent during recruiting.
However, by partnering with a PEO or staffing agency through a co-employment arrangement, smaller companies can suddenly provide very enticing benefits packages on par with bigger industry players.
How is this possible? PEOs and agencies pool employees from multiple client companies when administering benefits plans. This increased scale allows them to secure highly competitive rates from insurers and other benefit providers — rates typically reserved for massive corporate clients.
In turn, the co-employer can pass those savings onto their clients, enabling even small or mid-sized businesses to offer Fortune 500-level medical/dental coverage, life insurance protections, 401(k) retirement savings options, and other perks that job seekers find hugely valuable.
Boosting their ability to provide attractive benefits helps smaller players bolster their employer brand and better compete for top talent against bigger companies. This represents a major selling point for entering co-employment partnerships.
While beneficial overall, some key downsides to consider:
When establishing a co-employed workforce, there are several key steps to take:
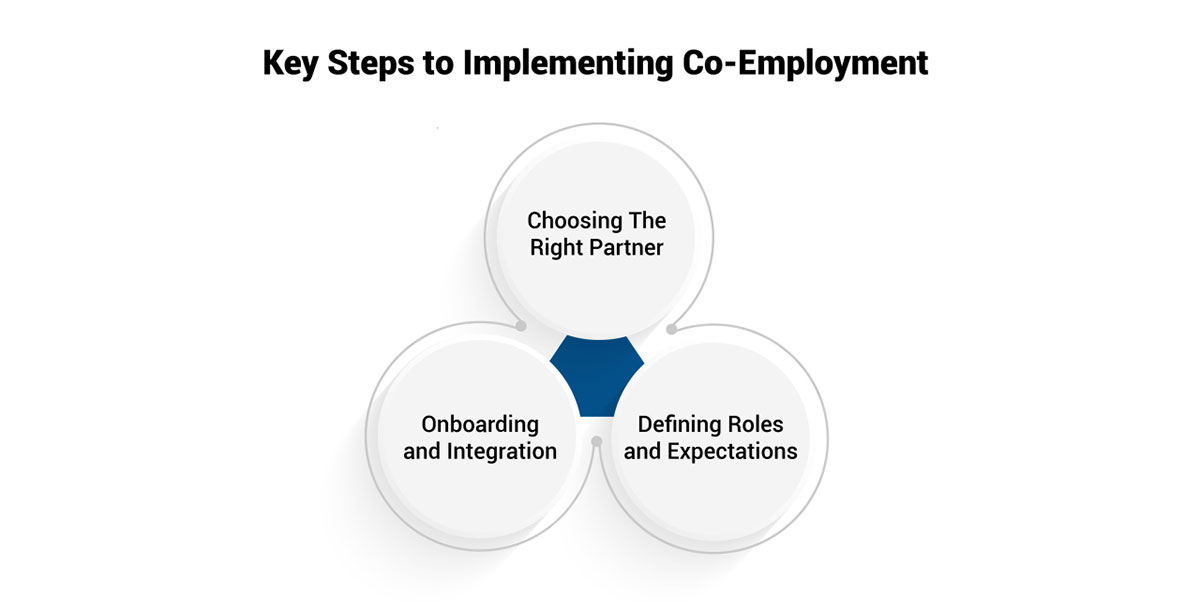
Conducting thorough research is essential when selecting a co-employment partner such as a professional employer organization (PEO) or staffing agency. It is crucial to take the time to assess potential partners and choose one that best suits your organization's specific needs and has a proven track record of success.
You'll want to carefully check references and reviews to verify their capabilities and reliability. Get insight into their level of expertise with handling critical HR functions like payroll processing, benefits enrollment, compliance practices, etc. Ensure they have experience working with companies in your specific industry as regulations can vary. Vetting potential partners thoroughly upfront helps prevent issues down the line.
Creating a comprehensive and detailed co-employment agreement is vital for clearly outlining the separation of obligations between you and your chosen partner. Clearly delineate who is responsible for specific employer duties like recruiting and hiring staff, managing employee relations, workplace safety protocols, leave administration, etc. Spell out expectations for frequency/methods of communication about employee issues.
Having clarity around roles prevents confusion and disputes later on regarding accountability. It also provides you with recourse if your partner fails to fulfill duties as outlined. Continually reviewing and updating the agreement as needs evolve ensures alignment.
Having a robust onboarding plan is key to successfully integrating any new hire, but even more so with a co-employed workforce. Work closely with your co-employment partner to develop orientation and training programs that immerse new staff in your organizational culture while also educating them on workplace policies. Your partner should provide support with paperwork, reviewing company guidelines, enrollment in benefit plans, etc.
Schedule regular check-ins during a new employee's first 90 days to address questions or concerns about roles, responsibilities, etc. Poor onboarding often leads to higher turnover, so dedicate sufficient focus here. A coordinated effort pays dividends through a more unified, productive workforce. Maintaining ongoing communication about training/development needs is key.
Smooth onboarding results in a unified, and productive workforce.
Once implemented, best practices for management include:
Consistent messaging between all parties is vital. Check-ins and meetings ensure everyone's aligned on responsibilities and priorities.
Manage employee performance collaboratively using aligned metrics and goals. Seek co-employer's input on training needs.
Establish constructive procedures to address disputes promptly. Document all decisions to prevent repeat issues.
Co-employment delivers optimal results by:
Choose an ethical, capable co-employment partner suited to your needs. Maintain open communication and transparency.
Regularly review arrangements and solicit feedback. Implement enhancements to workflows, training and technology.
Keep updated on employment law changes that could impact policies and procedures. Seek specialist guidance.
By selecting the right partner, defining roles clearly, integrating people and processes, and proactively collaborating, companies can maximize the benefits of co-employment while minimizing risks.
It's an arrangement that offers outstanding advantages, but careful implementation is key to reducing liability and amplifying rewards. Use these guidelines to set your co-employed workforce up for success.