
The world of work is transforming at an unprecedented pace. Automation, digitalization, demographic shifts, and market volatility are continuously reshaping job roles and skill requirements. This dynamic landscape demands that talent strategies keep up to access and retain skilled workforces that can steer organizational success. An approach that is gaining swift dominance in enabling workforce agility and resilience is a skills-first model for talent management.
A skills-first approach refers to talent acquisition, development, and deployment practices that prioritize candidates’ proven skills and abilities over parameters like formal qualifications, pedigree, and tenure. This model shifts focus from merely ‘doing’ a job to being adept at it through continual skill cultivation mindsets and systems.
By moving proven competencies to the center of talent processes from hiring to upskilling, a skills-first paradigm nurtures high-impact workforces ready for fluid business environments. Let’s examine why skills-first is mission-critical for future success.
Volatile, uncertain business conditions globally, coupled with breakneck technological progress, make adaptability an existential need. Companies must build responsive workforces that can rapidly evolve skills and behaviors to seize fleeting market opportunities. Three compelling trends underscore an organization-wide skills orientation for survival.
As per ManpowerGroup’s 2023 Talent Shortage Survey, companies globally face the worst talent shortage in over a decade at 75%. With over 8 in 10 employers reporting difficulty filling jobs, skills deficits severely undermine performance. Focusing intentionally on competencies addresses hiring gaps better.
Automation, digitization, and emerging roles radically alter skill relevancy cycles. Technical skills now have half-lives as short as 2-3 years. Continuous reskilling and up-skilling are mandatory. Honing a culture focused on skills enables nimble adaptability.
Aging workforces and low birth rates are shrinking talent pipelines, further exacerbated by early retirements due to the pandemic. This makes skills-based hiring key to tapping wider talent pools. Millennial and Gen Z workers prioritize career growth opportunities, which skills-focused employers provide better.
Implementing a Skills-First Approach holistically, from hiring and mobility to development and culture, fosters durable organizational viability amidst talent management skills scarcity and uncertainty.
Let’s explore six essential steps to implement a skills-first recruiting approach.
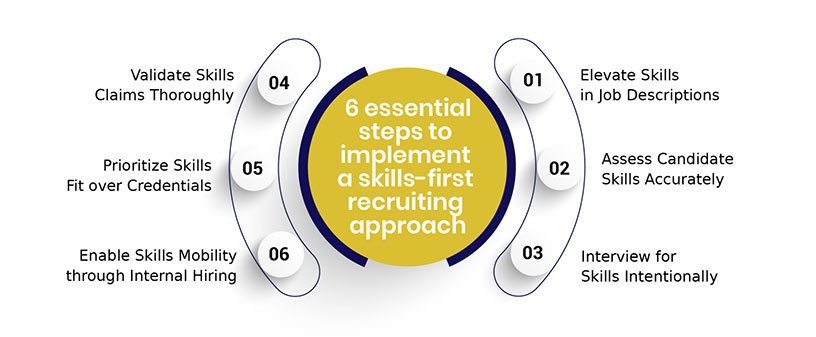
Traditional job descriptions emphasizing formal qualifications and prior industry experience restrict applicant pools unnecessarily. Prioritizing skills and competencies over pedigree expands access to talent with transferable abilities to succeed despite different backgrounds.
Evaluating skills objectively is crucial for aligning candidates with role needs. Methodical assessments of strengths and development areas through reliable psychometric tests, simulations, micro-projects, etc, surface competencies accurately for hiring fit.
Skills-based interviewing using structured, competency-based techniques assess applicants’ expertise. Crafting skill-revealing questions aligned to essential role capabilities filters candidates effectively vs just focusing on work history.
Creating Composite Skills Scorecards standardizing key role competencies aids skills verification across applicants. Supplementing self-reported assertions of competence with discreet validation checks enhances truthfulness for hiring.
By definition, a skills-first paradigm hires for proven talents over degrees alone. Expanding eligibility beyond conventional education requirements provides overlooked competent candidates with hiring opportunities.
Skills-first hiring should encompass robust internal mobility programs for fulfilling open positions preferentially through upskilled internal candidates. This amplifies retention while reducing time and risk.
Hence, implementing skills-first recruiting delivers compounding advantages spanning superior hiring decisions, cost savings, and retention values for enduring success.
With automation replacing some 85 million jobs by 2025, continual reskilling is mandatory for organizations to remain competitive.
Strategic skills development calls for:
Creating organization-wide Skills Inventories providing profiles of workforce capabilities and development areas allows targeted, aligned learning initiatives for closing gaps.
Leveraging labor market insights to identify emerging in-demand skills helps get ahead of external changes to build future-ready workforces proactively.
Selecting training content directly relevant to employee or team skill needs using insights from skills assessments tightens capability building efficacy.
Using digital channels like mobile microlearning, AR/VR simulations, and AI-based personalization for distributing training aids easy, economical access for employees as per preferences.
Empowering employees to select skills training to align with personal growth goals boosts motivation and capability augmentation manifold owing to intrinsic desire.
Assessing skill application on-the-job post-training using observation, surveys, and metrics confirms learning transfer for tangible productivity improvements.
Together, these pillars of dynamic skills development enable building workforces with sharpened, market-aligned capabilities continually for sustained value delivery.
With confidence in career progress opportunities being the prime talent retention driver today, skills-first development is key for retention. Strategies like:
Exposing high performers to vacant positions matching their skills provides valued career development, reducing external departure risks.
Paying for applicable skills boosts the financial upside for skill mastery. Popularized by tech majors like Microsoft, skills allowances build employee loyalty.
Clear pathways for elevating expertise via credentialing, stretch assignments, and managed learning nurtures talent retention by signaling competence improvements.
Celebrating new skill gains publicly fosters positive reinforcement for persevering at capability enhancement in contrast to only praising output.
Thus, nurturing meritocracy and development oriented on personal mastery cements retention synthetically.
Ultimately, organizational culture alignment is imperative for skills centrality to endure as a driver of agile people strategies delivering consistent advantage.
Tactics to achieve this include:
Frequent communications from senior executives highlighting skills importance sets priorities for managers on competency building expectations and reviewing skills progress.
Identifying skills-oriented team members at all levels as evangelists through training on conveying skills and values acts as influencers guiding cultural transition through peer advocacy.
Collaterals creatively positioned across offices explain skills-first principles using minimal text, engaging visuals, and provocative questions, sparking intrigue on skills and helping workforce mindset shift subtly.
Gamification keeps concepts intriguing for longer. Creative skills showcased through hackathons, skills masterclasses, and project presentations maintain engagement on capabilities uplift.
Thus, surrounding workforces with constant skills-related triggers embeds competence uplift as a cultural cornerstone for enduring unity on talent development.
Despite the immense potential, skills-first faces adoption barriers requiring mitigation for smooth deployment. Common hurdles include:
Intangible abilities like creativity, empathy, and judgment, though critical, remain difficult to size up reliably during selection. Holistic evaluation techniques combining psychometrics, case studies, and references help.
With no formal mastery certificates for many emerging domains like data science or UX design, confirming proficiency levels is complex. Detailed technical discussions, simulations, and tests aid authenticity.
Continuous capability enhancement needs significant investments, especially for customer-facing employees. Gradual implementations first limited to revenue-impacting roles manage spend.
Traditional education-reliant leaders may underappreciate skills centrality, which prolongs outdated practices. Patient dialogs, external best practice sharing, and skills analytics help convince skeptics.
Thus, acknowledging inevitable hurdles expected when transforming talent strategies allows pragmatic change management for smoother skills-first acceptance.
In an uncertain world, organizational viability hinges on nurturing adaptable and skilled workforces able to evolve dynamically. Skills-first talent strategies that hire for competencies, develop skills continually, and reward mastery foster such agility for sustained market leadership.
While the road may have implementation bumps, the destination promises rich rewards for workforce capabilities, empowerment, and competitive advantage. The future undoubtedly belongs to talent leaders pioneering a skills-first paradigm today.