
A skilled, motivated workforce is undoubtedly every organization's most valuable asset. But even the best teams may not always have capabilities fully matching evolving business needs. This is where conducting a structured skills gap analysis provides data-backed insights guiding strategic upskilling, hiring, and capability building to bridge the divide.
This guide offers a comprehensive perspective on skills gap analysis - what it entails, types of approaches, steps for effective employee assessment skills, and how findings activate meaningful workforce development, unlocking individual and organizational success.
The skills gap refers to the disparity between current talents and abilities of the workforce versus those required for successfully executing roles, responsibilities and business objectives.
In simple terms, it means employees do not have the abilities needed to do their jobs well. There can be gaps for many reasons. Such as when a company moves into new markets, uses advanced technology, changes workplace policies, or updates business goals.
Skills gap analysis is a thorough process to:
Make sure accountability measures are in place for closing prioritized gaps within reasonable timeframes.
Taking a structured approach to regularly assess critical skill levels across teams allows organizations to:
In essence, skills gap analysis provides data and insights required to have a resilient, future-ready workforce able to achieve evolving organizational strategies and growth priorities.
It enables constructing a realistic skills-based employee development roadmap aligned with strategic business objectives. The outcome is an empowered, competent talent pool equipped with the evolving expertise and experience needed to drive innovation and organizational success.
Skills gap analysis can be qualitative, quantitative or a team approach suiting analytical needs.
A qualitative skills analysis uses descriptive labeling for evaluating employee proficiency like “Expert”, “Competent” or “Basic” across listed skills. If the employee's skills are labeled as "basic" or "competent" instead of "expert" for something important, then that shows a skills gap. Some common methods include:
Qualitative analysis provides a quick overview of skills gap. But different managers may use the rating words differently.
For standardized objectivity, quantitative skills analyses assign numeric scores reflecting ability levels - such as 1-Beginner, 5-Expert across listed skills. Statistical analysis on scores gathered through:
Data is systematically benchmarked against requirements to reveal gaps. While intensive, quantitative findings provide consistent talent insights. The outputs also integrate well with modern HR information systems and people analytics tools to enable tracking and time-series based monitoring of the team.
Team skills analysis focuses on whether a team has all the required skills for a particular project or task coming up.
For example, does the marketing team have competencies like writing, graphic design, analytics, social media, and digital advertising needed for the campaign?
If the analysis finds gaps like no strong writer, then they may need to bring in a new team member or outside freelancer to fill that hole.
Team analysis helps managers optimize skill coverage across a group working closely together towards a common goal. Addressing weak spots ensures better team performance.
The skills gap analysis process involves sequenced steps centered on maintaining alignment with evolving organizational business objectives. Let's explore the key steps to conduct impactful skills assessments.
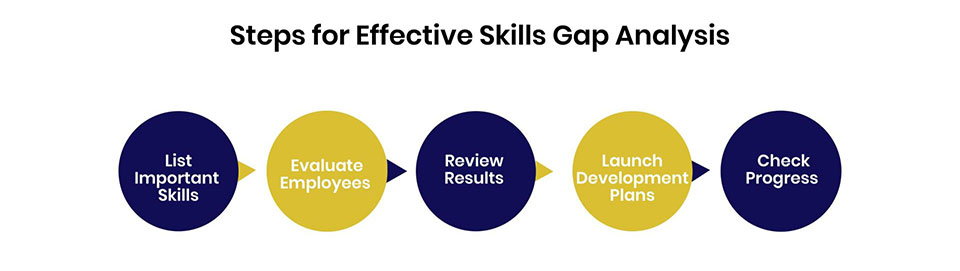
Create a list of competencies to evaluate across:
Solicit input from business leaders, functional heads, and employees on priority skills to shape assessments.
Provide clear definitions of competencies to enable accurate evaluations. Sort into primary and secondary focus areas.
Assess employee skill levels across listed competencies using:
Managers closely working with employees can provide the clearest insights. An unbiased external evaluator further enhances objectivity.
Apply consistent measurement tools across the organization. Customize only the skills domains by role type. Provide grading rubrics for reliable results.
Hold review discussions on individual skill gaps. Develop mentoring, training, and on-the-job development plans to close prioritized gaps through guided progression. Get employee input on growth needs during the review.
Additionally, analyze company-wide trends to identify strengths, high risk areas and inform large scale development investments.
Use tailored methods to address gaps such as:
Consider external recruiting or contractors to fill difficult voids in specialized competencies.
Also, update hiring practices to source candidates with key emerging skills. Maintain a healthy mix of internal development and external hiring.
Periodically re-evaluate employees against key skills measures using consistent tools to confirm improvement and analyze growth trends over time.
For example, assess high-priority skills more frequently, like every quarter. Evaluate other competencies on a six-monthly or annual basis.
Help employees sustain capability advancement by defining next-level skills targets once current gaps close. Make development an ongoing process.
The key is keeping the focus on a few critical skills, collecting consistent measurements, and creating customized development plans to boost skill levels. Review regularly to check progress.
In conclusion, a skills gap analysis compares employee competence to the level needed. It informs training and hiring to boost capability across individuals, teams, and the whole company. Regular checks ensure you address ever-evolving needs proactively.
Invest in your people's growth. Employees staying relevant through purposeful development are every organization's vital competitive edge today and pivot readiness for tomorrow.