The Changing Role of E-learning in Employee Development
August 12, 2024

E-learning has become an important tool for employee development in modern organizations. With the proliferation of internet and mobile technologies, e-learning allows businesses to provide continuous training and development opportunities to employees in a flexible, engaging and cost-effective manner.
This article discusses how e-learning supports employee development through personalized learning, flexible accessibility, improved knowledge retention, cost-effectiveness, mobility, collaboration and detailed analytics capabilities. It explores the role of e-learning in career development and retention of talent.
What is E-Learning?
E-learning refers to the use of electronic media and information and communication technologies in education. It delivers flexible learning through digital tools like LMS, video, audio, simulations and games. With e-learning, training can happen anywhere, anytime through the internet or intranet. It provides self-pace as well as live instructive learning.
Benefits of E-Learning for Employee Development
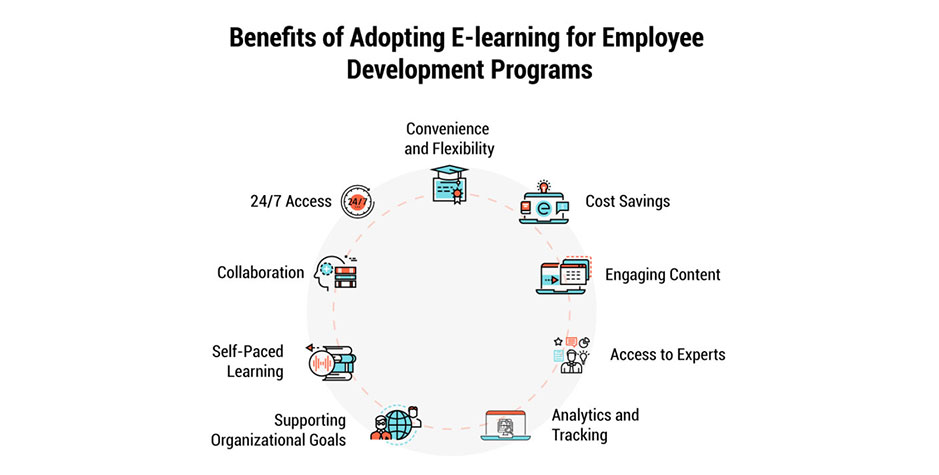
Some key benefits of adopting e-learning for employee development programs include:
-
Convenience and Flexibility: E-learning allows employees to access training modules as per their schedule and pace of learning. They can resume interrupted sessions and revisit content as needed. This flexible approach addresses the unique needs of a diverse and geographically distributed workforce.
-
Cost Savings: E-learning eliminates the cost of organizing classroom training including venue, travel etc. It can be easily scaled up without increasing infrastructure costs. Training resources can be reused, and updated and content development is more cost-effective compared to traditional methods.
-
Engaging Content: Through multimedia, interactivity, social tools and gamification, e-learning keeps employees engaged for longer periods. Techniques like microlearning and bite-sized content help retain attention. Leaderboards, badges and competitions in a gamified approach motivate self-driven learning.
-
Access to Experts: Recorded video lectures, webinars and virtual classrooms help bring globally renowned subject matter experts to employees across locations. Learners can ask questions, take virtual tours and seek help from instructors and peers online.
-
Analytics and Tracking: E-learning platforms capture data about course completions, time spent, performance, areas of weaknesses etc. This helps measure the impact, identify knowledge gaps and track individual progress. The insights aid in competency management and skill development initiatives.
-
Supporting Organizational Goals: Training content in e-learning can be tailored to specific job roles and align with the strategic priorities of the company. Learning objectives, assessments and certifications ensure employees attain the competencies required to achieve business targets.
-
Self-Paced Learning: Employees get the flexibility to learn at their own pace, revisit resources and schedule practice sessions. They can explore additional recommended content to expand and update skills according to their needs and interests. Competency frameworks provide transparency in skill requirements.
-
Collaboration: Through online forums, social networks, peer helping and file-sharing tools, employees connect with each other for discussion, clearing doubts and exchanging ideas. This helps apply learnings from the classroom to real work scenarios.
-
24/7 Access: Employees can log in and resume learning from any place and via any compatible device like desktop, laptop, tablet or mobile as per their convenience. This allows people with varying schedules and locations to complete mandatory training modules.
Tools for Employee Development
Organizations utilize different e-learning tools to develop skills and empower employees:
-
Learning Management System (LMS): An LMS acts as a central online platform to enroll learners, and deliver and track training programs. It helps create, publish and manage digital content and certify completions.
-
Microlearning: Short interactive modules focus on specific skills. Bite-sized lessons retain attention for quick refreshers and on-the-job learning.
-
Social Learning: Discussion forums, groups and activity streams encourage peer-to-peer learning. Employees share experiences, and resources and collaborate online.
-
Simulations and Virtual Reality: Immersive simulations replicate real work environments to apply and reinforce learnings from safe, interactive practice sessions.
-
Video and Audio Content: Recorded lectures, interviews, and podcasts make dry content more engaging. On-demand access allows learning at one’s own pace.
-
Assessments and Gamification: Quizzes, tests, leaderboards, digital badges, and points-based systems turn learning into a competitive, rewarding experience.
-
Artificial Intelligence: AI evaluates learning patterns and recommends personalized paths. Chatbots provide 24/7 support for clearing doubts and ensuring deadlines.
-
Mobile Apps: Learners use intuitive responsive apps on all devices for quick reference, skill tests and microlearning on the move.
Key Elements of Successful E-Learning Programs
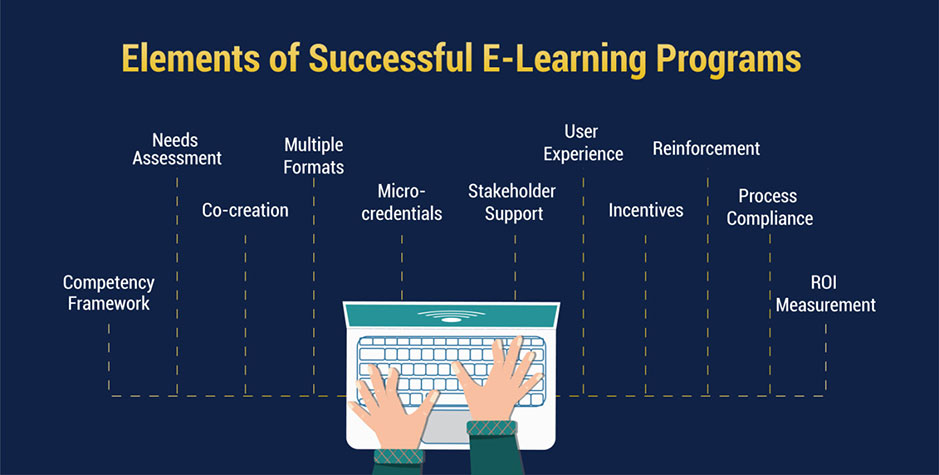
To ensure e-learning initiatives effectively contribute towards employee development, companies must focus on certain critical aspects:
-
Competency Framework: Define clear learning competencies and career paths aligned to business goals. This provides direction to the learning function.
-
Needs Assessment: Analyze skills gap and understand roles and desired proficiencies through surveys and feedback. Design relevant, targeted content.
-
Co-creation: Involve SMEs, managers and learners themselves in curriculum design, pilot tests and content updates for better adoption.
-
Multiple Formats: Employ varied formats like text, videos, and games to suit all learners’ preferences and optimize engagement. Offer self-paced, live and blended mode options.
-
User Experience: Prioritize intuitive navigation, responsive design, and performance on all devices and platforms to simplify UI/UX.
-
Micro-credentials: Issue digital badges or mini certificates on completion of modular programs for motivation and recognition.
-
Incentives: Appreciate active participation through rewards, gamified points/levels, promotions or salary hikes linked to new skills.
-
Reinforcement: Encourage regular refresher training and on-the-job practice supported by performance reviews and mentoring.
-
Process Compliance: Track attendance, submissions, and certification status to ensure timely completion of mandatory and role-based compliance modules.
-
ROI Measurement: Quantify outcomes like productivity increase, reduced costs, and higher satisfaction through metrics like pre- and post-assessments.
-
Stakeholder Support: Gain commitment from top leaders and allocate dedicated teams for content updates, tech support and the success of the digital learning initiative.
E-learning platforms can empower employees at different career stages with relevant and engaging resources. When designed well and aligned with organizational objectives, e-learning proves effective in developing a future-ready workforce through continuous skill enhancement.
Impact of LMS on Employee Development
Improving Skill Development and Retention
Learning management systems (LMS) promote employee skill enhancement and retention by providing centralized access to comprehensive training resources and analytics. Through an LMS, employees can develop in-demand qualifications by engaging in role-specific or elective training modules at their own pace. Personalized learning paths tailored to employees' roles, skill levels and career goals help close competency gaps. By addressing skills needs and supporting career mobility, LMS fosters a positive learning culture by retaining top performers.
Enhancing Performance and Productivity
LMS strengthens the link between learning and performance. Competency frameworks mapped to role profiles via LMS identify training impacting key result areas. Automated pre-and post-training assessments within LMS gauge learning and apply insights to enhance performance management.
Real-time LMS reporting gives managers visibility into team training for course correction. Gamification features in LMS motivate employees towards performance-linked learning goals. Feedback mechanisms empower peer-to-peer or automatic feedback, improving faster. Outcome-based LMS improves quality assurance through outcome-focused training adherence visible to quality auditors. Learning analytics compiled by LMS correlates training inputs with business outputs revealing top training investments.
Future Trends in LMS for Employee Development
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning expand LMS capabilities. Predictive algorithms analyze user-profiles and past interactions to personalize the learning experience. Banks can leverage AI to suggest courses based on each user's department, experience level and past training. This can improve course completion rates. AI assists in automated course building by using natural language processing to extract lessons from large datasets. AI also enables intelligent notifications prompting users to complete upcoming or overdue courses.
Virtual and Augmented Reality
VR and AR make training more engaging by simulating real work environments. An oil company developed VR safety training replicating rig conditions with hazards to identify. This led to a reduction in incidents compared to traditional e-learning. VR is also being applied to soft skills like emotional intelligence. Repetition allowed through VR cements learnings like empathizing with customers. AR enhances on-the-job training through assisted reality features like step-by-step instructions, checklists and multimedia reference guides accessible through AR devices.
Focus on Soft Skills Development
Soft skills are becoming a priority as these skills often determine career progress more than technical expertise. LMS assess and develop soft skills through simulations, role-plays, peer feedback and competency-based gamification. At a manufacturing firm, modules on communication, critical thinking and conflict resolution delivered via the LMS increased supervisor promotion rates. Social and collaborative features foster relationships and leadership through online communities, peer-to-peer learning and rotatory mentoring programs. Soft skills LMS track intangible traits and their application reinforcing identified strengths.
Conclusion
In conclusion, LMS is revolutionizing e-learning in employee development by optimizing access to learning, enhancing skills that boost performance and retention, and leveraging emerging technologies. By centralizing training resources, mapping competencies, conducting analyses and implementing an outcome-focused culture, LMS empower employees to continuously upgrade their skills aligning individual and organizational objectives. The future of LMS lies in predictiveness to personalize learning paths and immersion through VR/AR to make training.
To succeed in today's dynamic workplace, organizations must adapt learning strategies to the rhythm of modern work and leverage LMS capabilities. By integrating LMS with HR processes and empowering employees as champions of self-guided evolution, the workplace can thrive with a multi-skilled, high-performance workforce that propels business growth. It is time organizations viewed LMS beyond learning and as a platform elevating the entire employee life cycle from recruitment to retirement. The seeds of competitive advantage are sown through the strategic use of employee-centric LMS.


