
An HRIS, or human resource information system, has become an invaluable tool for HR teams seeking to optimize efficiency, comply with regulations, and get a holistic view of their workforce through HR analytics. However, with many solutions now available, selecting the right HRIS for your needs and smoothly implementing it can seem daunting.
This comprehensive article will walk you through the key considerations and best practices for choosing and integrating an HRIS that meshes with your goals, existing tech stack, and organizational culture.
An HRIS, or human resource information system, is a powerful piece of software that helps automate, organize, and analyze employee data in one centralized platform to optimize an organization's HR operations. Core HRIS capabilities include:
While HRIS systems were traditionally focused purely on transactional activities like recordkeeping, modern solutions also incorporate more strategic elements like people analytics, allowing for data-backed talent decisions.
The right HRIS saves HR teams time on administrative tasks, ensures compliance, and provides holistic workforce insights to leadership—leading to happier, more productive employees.
Some of the major ways a Human Resources Information System can benefit an organization include:
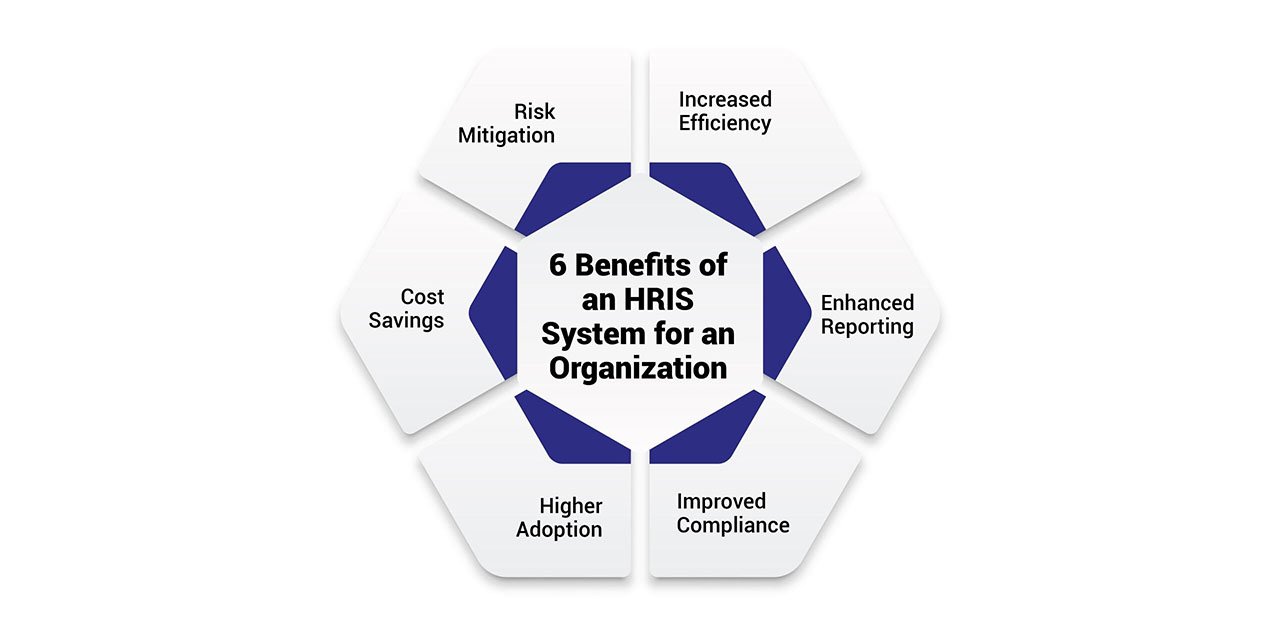
An HRIS automates many of the repetitive, manual processes that have traditionally consumed a significant amount of HR staff's time. This includes activities like payroll processing, benefits enrollment and changes, PTO tracking, candidate application review, performance reviews, and more. By digitizing and automating these tasks, HR professionals are freed up to focus their efforts on more strategic priorities.
For example, rather than spending hours inputting payroll data, the HRIS seamlessly transfers hours logged in the time tracking system and automatically applies salary info, tax rates, deductions, etc. to generate payroll. Employees can also make simple changes like updating contact details or benefits selections themselves via self-service portals rather than submitting forms to HR. This enables HR staff to dedicate their bandwidth to bigger-picture talent initiatives surrounding recruitment, development, retention, company culture, and more.
A major benefit of an HRIS system is its ability to aggregate and analyze HR data to uncover valuable insights. Rather than relying on manual reports cobbled together sporadically, HR leaders can leverage the system to access real-time analytics on critical workforce metrics. These include headcount by department, diversity statistics, salary expenditures, turnover rates, pipeline recruiting activity, employee satisfaction levels, and more.
The HRIS also empowers creation of custom reports tailored to the organization's specific areas of focus. These robust reporting capabilities enable data-driven decision making on HR issues. For example, talent acquisition teams can optimize their recruiting funnels based on metrics indicating where candidates tend to drop out. Total rewards specialists can model different compensation scenarios to refine budgets or test impact on retention rate projections.
HR departments are responsible for ensuring compliance with a complex web of federal, state, and local labor regulations. An HRIS centralizes and systematizes employee records, helping guarantee accurate tracking of data needed to meet compliance demands like required leave policy adherence, diversity reporting, pay equity enforcement, and more.
The systematized collection of employee data reduces potential for human error that could cause costly fines should inaccuracies occur. It also includes built-in rules and validations that align with legal standards, acting as a safeguard against potential infractions. With this improved compliance infrastructure, organizations mitigate risk while HR staff avoid frequently needing to double back and fact check records.
Unlike manual or siloed digital systems, an HRIS consolidates pertinent employee information and necessary tools into a centralized hub accessible across devices. This empowers employees to complete transactions at their convenience without waiting for brochures detailing benefit plans or meeting with HR to request basic changes. Instead, they can access pay stubs, tax forms, leave balances, enrollment forms, and more directly through employee login portals.
Higher adoption rates free up HR personnel bandwidth while also improving the broader employee experience. Enabling employees to easily update life event changes, check required information, and complete tasks on their own schedule demonstrates an investment in trust and autonomy. This contributes to overall employee satisfaction, engendering higher motivation and performance levels.
Transitioning from manual processes to an automated HRIS produces measurable cost savings over time. Consolidating systems leads to lower software, maintenance, and troubleshooting costs rather than expenses for individual niche solutions. Automating repetitive tasks reduces needs for large HR back-office administration teams, leading to lower HR overhead. Digitizing processes also cut the volume of materials like printing paperwork for storage or mailing lots of enrollment packets.
An HRIS also minimizes compliance infractions that would incur costly legal penalties or settlement fees should inaccurate employee data fall out of compliance. And likely most significantly, the streamlined structure empowers strategic HR direction to boost productivity, performance management, and employee retention. This drives revenue by catalyzing innovation and growth rather than getting sidelined managing paperwork or routine tasks.
Centralizing and systematizing HR processes and data mitigates risk on multiple fronts. First, it reduces the potential for human errors leading to inaccurate employee records that could cause compliance violations. Data validation controls also minimize bad data entry. Process automation limit's the ability for drops in protocol like missing deadlines for reporting payroll taxes.
It also ensures continuity of operations should personnel change occur. Unlike knowledge kept in individuals' heads or stored sporadically across local desktops, the HRIS creates an accessible centralized repository for the full employee record. So, if someone leaves the company or transfers departments, the next person can get quickly up to speed without piecing together scattered documents and possibly missing information.
With the right solution catered to your needs, an HRIS delivers immense value. Now let’s explore finding the ideal match.
Selecting a Human Resources Information System that aligns with your organization’s requirements, existing tech stack, and budget can be challenging. Follow these best practices when evaluating options:
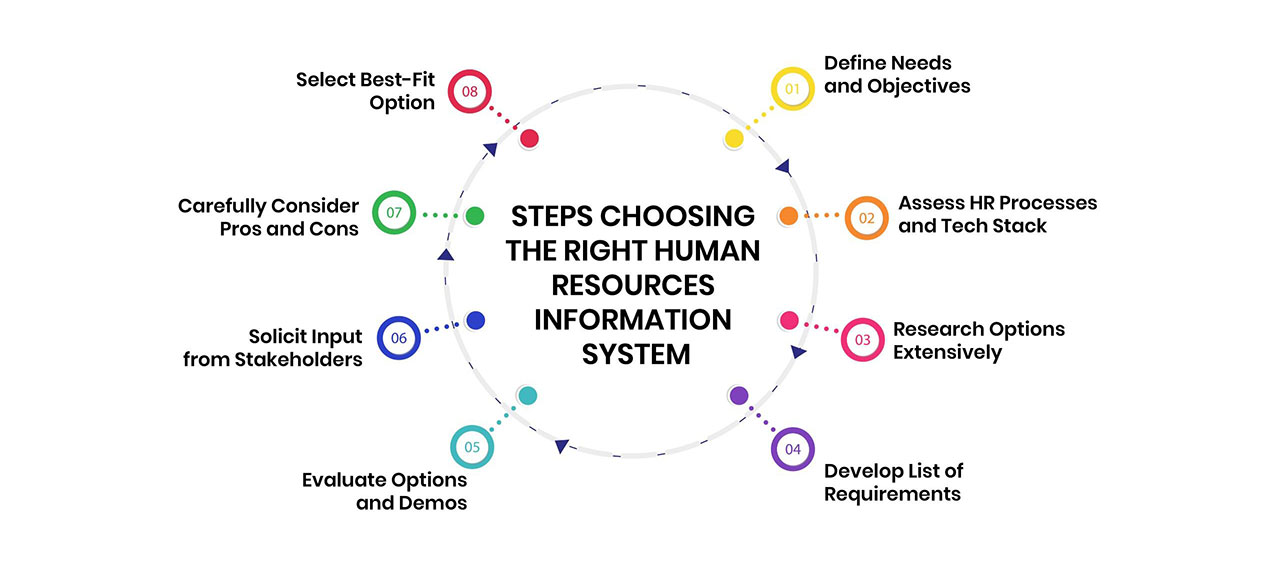
Having a clear vision of your goals and top priorities for implementing an HRIS is crucial. Questions to consider:
Getting input from the stakeholders across the business provides a helpful perspective. Keep end user experience top of mind.
Take stock of current HR workflows and tools, identifying process inefficiencies, gaps in systems, and pain points for users. An HRIS can maximize value by integrating with your existing HR tech stack through APIs.
If multiple disjointed systems are currently used across recruiting, payroll, learning management etc, consolidating onto a unified HRIS platform brings immense benefits.
The Human Resources Information System marketplace offers diverse solutions catering to organizations of all sizes and industries. Conduct extensive research to create a shortlist of top contenders.
Aspects to compare include:
Compile a detailed list of your features, integration, and configuration requirements so vendors can provide accurate quotes.
Requirements gathering gives a concrete picture of must-haves for a seamless HRIS that adds value across the employee lifecycle.
Prioritize capabilities that solve defined problems and enhance productivity through automation. Seek tools purpose-built for HR that allow customization.
With your documented criteria, systematically assess contenders that seem poised to address prioritized requirements across features, security, support, ease of use and cost.
Some markers of HRIS vendors truly invested in your success include:
Be wary of vendors either not listening to your goals, overpromising with unsupported claims, or pushing one-size-fits-all solutions unlikely to match unique needs.
After narrowing down the field, schedule demos from three to five leading choices. Prepare detailed questions related to your defined requirements and priorities.
Request access to software trials or sandboxes whenever possible to tangibly assess firsthand. Vet how easily tasks can be accomplished.
Gather regular feedback from HR leadership, IT teams, department heads and employee focus groups during the evaluation process.
Incorporating insights from diverse end users leads to greater buy-in and adoption success. The most well-rounded perspectives come from blending viewpoints across roles and seniority levels.
With help from stakeholders, compile pros and cons checklists for the top solution candidates under consideration using the needs analysis and hands-on research as reference points.
Compare options across these aspects:
Keep focusing squarely on your organization’s concrete needs and which vendor offers the strongest partnership. Declutter from flashy features unlikely to provide ROI.
With thorough research and input from diverse end users, the HRIS choice delivering the maximum bang for your buck should rise above the pack.
Confidently investing in an adaptable platform poised to solve problems unique to your culture and processes pays dividends. But proper implementation ultimately determines ROI realization.
Once the Human Resources Information System purchasing decision is made, integrating the new system smoothly across departments ensures it takes hold and drives the desired business outcomes. Here are the steps for a successful HRIS implementation:
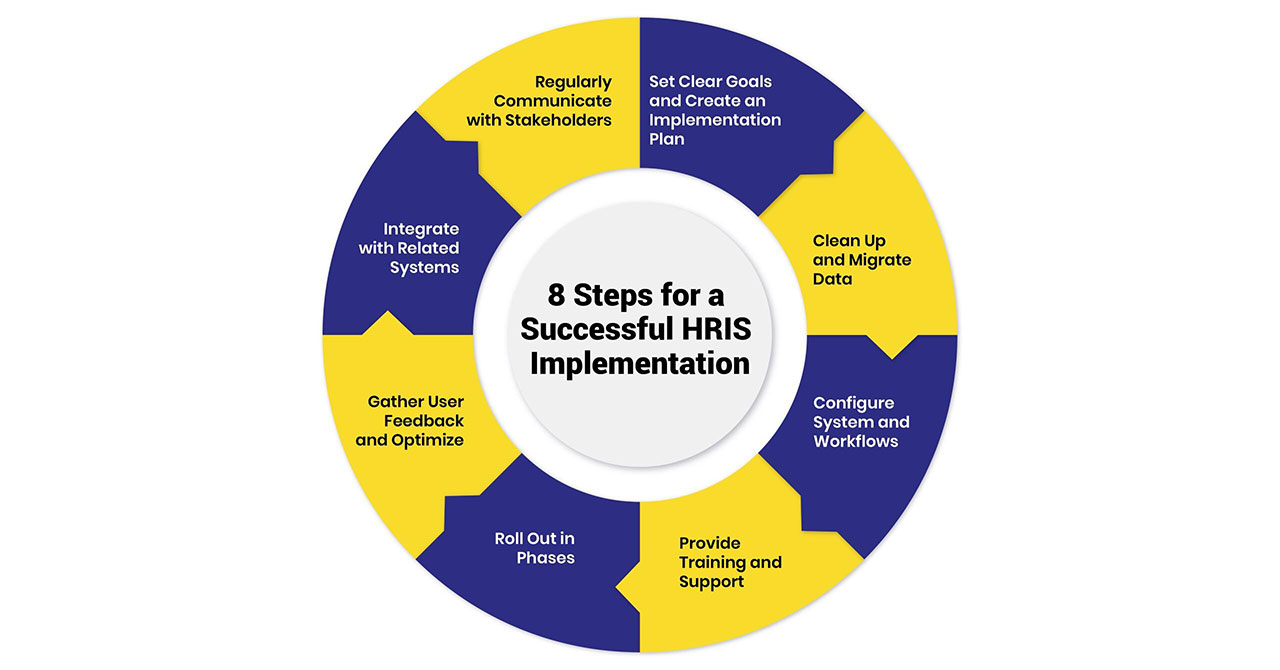
Before beginning the HRIS implementation, clearly define the objectives you want to achieve and create a comprehensive plan. Outline the scope, major milestones, roles and responsibilities, timelines, training requirements, and measures for success.
Involve stakeholders from HR, IT, finance, operations etc. to get buy-in. Appoint an implementation manager to lead the project. Setting clear goals and outlining the activities upfront ensures all teams are aligned for a smooth rollout.
Data migration is one of the most crucial and time-intensive aspects of HRIS implementation. Start by auditing and cleansing existing HR data from multiple systems and spreadsheets. Eliminate duplicates, fill gaps, and fix inaccuracies to create a single source of truth.
Work closely with the vendor to securely migrate clean data into the new HRIS. Validate accuracy post-migration through test runs before going live. Investing effort upfront to migrate high-quality data minimizes issues down the road.
Based on your business requirements, work with the vendor to configure the HRIS architecture, interfaces, fields, forms, workflows etc. Balance customization with adaptability to the vendor’s best practices.
Testing configured workflows extensively before rollout allows you to iron out issues proactively. This step lays the critical groundwork for user experience and functionality.
Conduct training workshops for all users, including hands-on system exposure. Training schedules should align with rollout timelines. Group users with varying learning curves into beginners and advanced classes.
Set up dedicated HRIS support teams for the initial few months post-implementation to help users navigate common problems. This accelerates user adoption and makes rollout smoother.
Big bang deployments tend to overwhelm users. Introduce the HRIS in phases – by geography, department, or function. This allows users to get comfortable with basic features first before moving to more complex modules.
Starting with smaller user groups also helps identify issues early before organization-wide rollout. Celebrate milestones through each phase to maintain momentum.
Solicit honest feedback from users through surveys and meetings post each rollout milestone. Monitor system usage data and bottlenecks to identify problem areas and training gaps.
Use insights to alleviate pain points through renewed training programs or system enhancements. Continuously optimizing the HRIS based on user input ensures maximum adoption.
While HR owns the HRIS, it must integrate tightly with related systems like payroll, talent management, IT service management etc. Establish single sign-on and seamlessly share relevant data across platforms using APIs.
This connectivity provides a unified experience and 360-degree view of employees across HR, finance, IT and other functions. Integrations also prevent data silos and duplication of efforts.
Through the lengthy implementation process, consistently communicate timelines, milestones achieved, issues faced, and value delivered to both end-users and executive sponsors.
Celebrate quick wins and highlight positive feedback to maintain enthusiasm around the rollout. This transparency fosters trust in the new system across the organization.
By executing these 8 steps, organizations can ensure successful implementation of HRIS and unlock immense value in enhancing workforce productivity and organizational outcomes.
Implementing a Human Resources Information System is a complex undertaking that requires careful planning, and continuous improvements after deployment. With robust preparation, understanding, and empathy towards end-user adoption, organizations can transition to an HRIS that centralizes information, optimizes processes, and elevates the employee experience. Though challenging, thoughtful HRIS implementation can transform HR operations and unlock long-term gains.